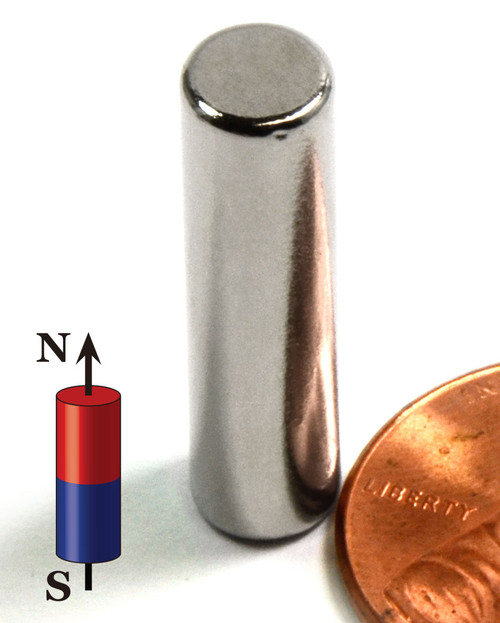
Product Description
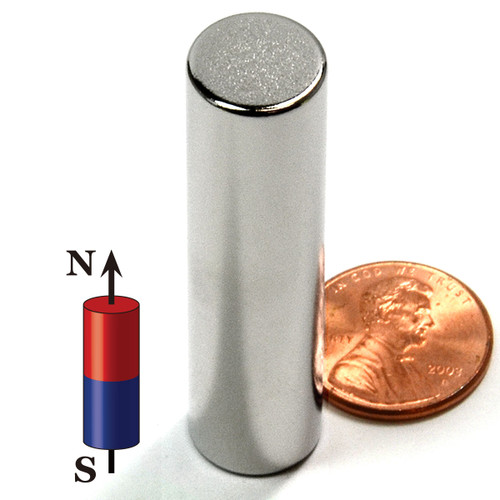
N52 Cylinder Magnet Dia 3/16x1/2" | Neodymium Cylinder Magnet | Small Cylinder Magnet | Rare Earth Cylinder Magnet
Features:
- Material: Sintered neodymium magnet, grade N52 rare earth
- Gauss Rating: 14,400 Gauss or 1.44 Tesla
- Pulling Force: 5.5 Lbs.
- Pole Orientation: Axially magnetized, the N and S poles on the two ends
- Coating: Ni+Cu+Ni 3 layer coated, the best coating available
- Tolerance: All are +/-0.002" with coating
- Applications: This cylinder magnet is great for industrial applications and personal projects
Warnings:
- All magnets may chip and shatter, but used correctly this cylinder magnet can last a lifetime
- Keep away from pacemakers and children
- If damaged please dispose of completely. Shards may be sharp and cut fingers
Product Links to Other Closely Related To Your Search
PLEASE NOTE: All magnets may chip and shatter, but if used correctly can last a lifetime. Keep away from pacemakers. Not for children, parental supervision strongly encouraged. COMMERCIAL USE ONLY. If damaged please dispose of completely. Shards are still magnetized and if swallowed can inflict serious damage if magnets join inside the digestive tract.
Neodymium Cylinder Magnets
Neodymium Cylinder magnets are used to make high end speakers, electric motors, magnetic levitation, magnetic jewelries and magnetic beaCylinders , etc.
See Our Pinterest Page For Some Great Project Ideas
Here at Magnets For Sale & CMS Magnetics we carry neodymium Cylinder magnets with epoxy coatings and with a countersunk hole already drilled in the middle to attach it to nonmetallic materials such as wood or plastic. These Cylinder magnets even allow the screw’s head to reside below or even with the face of the Cylinder magnets to ensure it does not interfere with the Cylinder magnet function.
See Our Pinterest Page For Some Great Project Ideas
Order your Neodymium Cylinder Magnets online or over the phone.
In this Cylinder magnet category, CMS has the Strong neodymium Cylinder magnets with epoxy coatings and Cylinder magnets with a countersunk hole already drilled in the middle to attach it to nonmetallic materials such as wood or plastic. This feature at least doubles their usefulness. These neodymium Cylinder magnets if equipped with countersunk.
These are rare earth super strong neodymium Cylinder magnets and is made for holding stuff & that is what they do they do best!
These are not the super strong neodymium Cylinder magnets you played with as children 15-20 times the force of those old time super strong neodymium Cylinder magnets. Never experienced Super powerful neodymium Magnetic Cylinders ? Now is the time! Our rare earth Cylinder magnets have a high saturation magnetization & tetragonal crystalline structure. Cylinders top physical pulling force & maximum energy product from these strong magnets . These hold very well against steel surfaces with direct touch and direct pull. The magnetic strength will last forever under normal use.
Many Uses & Users For A Cylinder Magnet
Cms magnetics’ super strong neodymium Cylinder magnets are used by school teachers machinists magicians engineers, students hobbyists inventors technicians DIYers Mars Rovers (yup up there) craft magnets uses hobbies therapy storage experiments science fairs magnetic bars labs garages schools offices refrigerator magnets & as a strong earth magnet
These powerful Cylinder magnets are comprised of strong neodymium material makes them the strongest Cylinder magnets of their size commercially available. These Cylinder magnets are axially magnetized so the north and south poles are on the flat surfaces, and the red line on one side of the Cylinder magnet denotes which side the north pole is on. Neodymium Cylinder magnets are strong magnets & are unique because of their extreme resistance to demagnetization. These Cylinder magnets will only lose their magnetism if they're heated above 176 degrees Fahrenheit. Our Strong Neodymium Cylinder Magnets have a special set of uses in the world of magnets. Cylinder magnets are specially suited to those magnetic repulsion experiments where you dangle 2 magnets from a string, but also Jewelry and in the medical field. One magician we know even wanted one that looks like a wedding ring. Hmmm, the methodology for the trick would be hiding in plain site.
About Neodymium In General
Neodymium magnets overall, are the world's strongest permanent magnets. Although, not all neodymium Cylinder magnets share the same characteristics. The Grade of a Neodymium Magnet will provide an idea of the strength of a neodymium magnet. The most common commercially available grades generally run N35- N52. N35 is the weakest (but by no means weak) and N52 is currently the strongest. There are some special use grades as well. A larger piece of neodymium of a weaker grade may be ultimately stronger than a smaller but higher grade piece. Our strong Cylinder magnets are designed & manufactured to meet stringent quality standards of both external and our own standards.
Neodymium Magnets are the popular choice for Homes, Work, Shops, DIY, Science, Hobby, Crafts, Office, Fridge, Science, Fair, Just Plain Fun, Alternative, medicine, Sorting metal items, Hold things up, Hold, things, down, Duvet, Cover, Closures, Hanging, Art, scarves, jewelry, belts, Handbags & Classroom Decorations.
Cylinder Magnets, Magnetics & Magnetism
This article will discuss the world of magnets from very different end users viewpoints. Firstly the article is addressed to someone in a high school or maybe a 101 level in college to aid them in navigating this part of physics. This portion of the article will also point to experiments that will demonstrate the points being made.
Secondly this post will address the “what does that mean to me?” group. Usually consumers of magnets whether they are a hobbyist searching for a small magnet to hand a photograph, an organizer searching for a way to straighten up a workshop or a manufacturer in search of enough magnets quickly to finish a current run on a manufactured product.
Some portions of this article came from Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia and are being used under the creative commons share & Share alike clause. Those portions may be used by anyone. Other portions belong to CMS Magnetics & Magnets For Sale & are copyrighted and may not be used without written permission.
Magnets This article is about objects, materials, devices that produce magnetic fields. Most of the subject matter here covers all Neodymium Cylinder Magnets . We will in many cases be using the term “Neodymium Cylinder Magnets” as the example, as this is the title & subject matter of this particular category.
The information given applies not only to the Neodymium Cylinder Magnets but the composition of all Neodymium Magnets .
Neodymium Cylinder Magnets are made of neodymium, an iron alloy. The Cylinder magnet, made in the shape of a Ring, the 2 magnetic poles in this case are through the thickness. This shape of a magnet make it very useful in both industry and by the casual consumer. The Cylinder Magnet’s shape is one of the major divisions of magnets. The Cylinder Magnet needs to physically fit where the consumer needs it to fit. Neodymium is a magnetic material that was applied to magnets in the 1980s. Neodymium is the strongest Cylinder Magnet in the world. Actually the material is the strongest permanent Cylinder Magnet in the world. The term “permanent” is just saying that you cannot turn it off & on at will as in an electromagnet.
Discovery And Development
Main article: History of electromagnetism
Ancient people learned about magnetism from lodestones (or magnetite) which are naturally magnetized pieces of iron ore. The word magnet was adopted in Middle English from Latinmagnetum "lodestone", ultimately from Greek μαγνῆτις [λίθος] (magnētis [lithos])[1] meaning "[stone] from Magnesia",[2] a part of ancient Greece where lodestones were found. Past civilizations learned of the existence of magnetism from, (curiously enough) a stone called magnetite (also called loadstone). This was naturally magnetized pieces of iron ore. Some of this loadstone dangling on a stCylinder was actually the first compass. So with this man had discovered that there was a connection between the magnetism in that little rock and the earth.
The earliest known surviving descriptions of magnets and their properties are from Greece, India, and China around 2500 years ago. By the 12th to 13th centuries AD, magnetic compasses were used in navigation in China, Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and elsewhere.
Measurement of Magnetic Strength
Magnetic flux density A vector quantity measures Cylinder the strength and direction of the magnetic field around a magnet.
Magnetic flux density also can be understood as the density of magnetic lines of force, or magnetic flux lines, passing through a specific area. It is measured in units of tesla. Also called magnetic flux.
Magnetic flux density is measured with a flux capacitor . The measurements may be in either Gauss or Teslas. Both of these measures are named after scientist in the field. A typical Gauss measure of a magnetic field of N52 ( the strongest Grade of neodymium may be 14,500 Gauss but measured in Tesla is 14.5 Tesla. The ratio is 1 to 1000.
Nikola Tesla 1846-1945 Worked with both George Westinghouse and Thomas Edison in the early years of electrifying America. He is known for his work in A.C. current and electromagnetism.
Fredrick Gauss 1777- 1855 was mostly a mathematician but also responsible for measurements of magnetic strengths.
The magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B field or just magnetic field, usually denoted B) is a vector field. The magnetic B field vector at a given point in space is specified by two properties:
-
Its direction, which is along the orientation of a compass needle.
-
Its magnitude (also called strength), which is proportional to how strongly the compass needle orients along that direction.
In SI units, the strength of the magnetic B field is given in
Magnetic moment
and source. If the field is uniform in space, the magnet is subject to no net force, although it is subject to a torque.[11]
A wire in the shape of a circle with area A and carrying currentI has a magnetic moment of magnitude equal to IA.
Detecting magnetic field with compass and with iron filings
Main article: Magnetic field
The magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B field or just magnetic field, usually denoted B) is a vector field. The magnetic B field vector at a given point in space is specified by two properties:
-
Its direction, which is along the orientation of a compass needle.
-
Its magnitude (also called strength), which is proportional to how strongly the compass needle orients along that direction.
In SI units, the strength of the magnetic B field is given in teslas.[8]
Magnetic moment
Main article: Magnetic moment
A magnet's magnetic moment (also called magnetic dipole moment and usually denoted μ) is a vector that characterizes the magnet's overall magnetic properties. For a aa Neodymium Cylinder Magnet , the direction of the magnetic moment points from the magnet's south pole to its north pole,[9] and the magnitude relates to how strong and how far apart these poles are. In SI units, the magnetic moment is specified in terms of A·m2 (amperes times meters squared).
A magnet both produces its own magnetic field and responds to magnetic fields. The strength of the magnetic field it produces is at any given point proportional to the magnitude of its magnetic moment. In addition, when the magnet is put into an external magnetic field, produced by a different source, it is subject to a torque tending to orient the magnetic moment parallel to the field[10] The amount of this torque is proportional both to the magnetic moment and the external field. A sphere magnet magnet may also be subject to a force driving it in one direction or another, according to the positions and orientations of the Neodymium Cylinder Magnets and source. If the field is uniform in space, the magnet is subject to no net force, although it is subject to a torque.[11]
A wire in the shape of a circle with area A and carrying currentI has a magnetic moment of magnitude equal to IA.
Warranty
This magnet includes a 10-year warranty for its magnetic strength, provided it is used under normal conditions. Usage in environments with elevated temperatures, significant vibration, or intense opposing magnetic fields will render this warranty null and void. It is also not suitable for use outdoors or in areas with high humidity or salt content, unless additional protective insulation measures are implemented.Product Videos
Custom Field
Product Reviews
6 Reviews
-
cylinders
This is a tiny n52 cylinder magnet and i works
-
Cylinder n 52
Very Strong and small
-
Worked superbly
I have had a CDI / Snap-on (from Brownells) torque screwdriver for years. The 1/4 bit holder magnet eventually broke into pieces. I contacted all three companies, and none of them stock this part for order separately. CMS to the rescue. I measured the opening, found exactly what I needed, and it just dropped right in. No glue was even needed. These are strong enough to stay in the bit holder, while still holding on to the 1/4" bits like a clamp. Thank you CMS! P.S. I will be alerting those companies that this product worked perfectly.
-
cylinders
I love magnets so much...it might be a bit of an obsession
-
cylinders
Used these to wipe my hard drive before letting my old PC go. Worked fine!
-
magnets
I order all my magnets from CMS. They have a good informative website, good product, price and great ship time.